Servicing a motor effected/washed by seawater:
- Cut out power supply by circuit breaker & taking out fuse. Mark & disconnect supply wire. Took Megger reading & recorded.
- Take out the motor, open up & dismantle. (Make sure marking on both cover & body)
- Clean and wash with warm fresh water.( About 180′ F)
- Cover by canvas, dry with positive ventilation & 500 watt lamp
- Clean with Electro cleaner.
- Baking by 500 Watt lamp for few hours.
- Take Megger reading. (test stable or constant reading) Apply insulation varnish to the winding while warm.
- Baking & taking the Megger.
- Reassemble & put back into service.
- When test run check sound, ampere & temperature.
Safety device on alternator:
- Heater
- Cooling fan.
- Reverse power trip.
- Preferential trip.
- Over current trip.
- Under voltage trip.
Windlass safety device:
- Slipping clutch.( Fitted between hydraulic motor and gear)
- Over load trip.
Winch safety device.
- Over load trip.
- Centrifugal brake.
- Magnetic brake.
- Limit switch for runner, topping & slowing.
- Hydraulic oil high temperature alarm & cut out.
- Hydraulic oil over head tank low level alarm.
Megger:
A Megger is an ohmmeter to measure insulation resistance in million of ohms. (Pole to pole, pole to earth). Good insulation has high resistance; poor insulation, relatively low resistance. The actual resistance values can be higher or lower, depending upon such factors as the temperature or moisture content of the insulation (resistance decreases in temperature or moisture).
Purpose of Megger Test:
- To verify insulation resistance.
- To detect any insulation fault.
Correct Procedure to Check Megger:
Switch off main switchboard by means of circuit breaker & taking out fuse, put label of MEN AT WORK, disconnect the connection from stator, teat with Megger Meter. Measure during hot condition resistance for accurate reading.
The Megger insulation tester is essentially a high-range resistance meter (ohmmeter) with a built-in direct-current generator. This meter is of special construction with both current and voltage coils, enabling true ohms to be read directly, independent of the actual voltage applied.
This method is non-destructive; that is, it does not cause deterioration of the insulation.
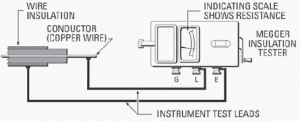
(Image Credit: electrical-engineering-portal.com)
Fig: Megger test instrument hook-up to measure insulation resistance.
The generator can be hand-cranked or line-operated to develop a high DC voltage which causes a small current through and over surfaces of the insulation being tested (Fig). This current (usually at an applied voltage of 500 volts or more) is measured by the ohmmeter, which has an indicating scale.
Safety device on switch board:
- Circuit breakers
- Over current relay (OCR) for protection from high current
- Reverse power trip
- Preferential trip
- Under voltage trip
- Fuse
- Earth lamp
- Synchroscope, synchronising lamp.
- Meter (ampere, frequency, volt, watt)
- Dead front panel safety device provided on the Main switch board individual panels wherein you cannot open the panel until the power of that panel is switched off.
Shore supply connections
- Where arrangements are made for the supply of electricity from a source on shore or other location a suitable connection box has to be installed in a position in the ship suitable for the convenient reception of flexible cables, it should contain a circuit breaker or isolating switch, fuses, and terminals of adequate size to receive the cable ends.
- For three phase shore supplies with earthed neutral terminals are to be provided for connecting hull to shore earth
- An indicator for shore side connection energised is to be provided.
- A means for checking polarity or phase rotation is to be provided
- At the connection box a notice indicating ships requirements with respect to supply as well as connection procedure.
- Alternative arrangements may be submitted for consideration.
How will you know the shore power supply is correct or not?
- Phase sequence indicator.(inside shore connection box, turn clock wise direction)
- Operate E/R vent fan & check airflow direction.
When excitation loss:
- Tapping with hammer to field coil core of excitation motor.
- Energise with battery.
Preferential trip:
If a generator overload condition develops, its preference overload trip will operate to energise the timing relay. The timing relay then operates to disconnect non-essential services in a definite order and at definite time intervals.
- None essential (without effecting the ship operation.) 5 sec:
- Essential (running the ship properly) 5 sec:
- Top polarity (propulsion, navigation) 15 sec:
Static electricity:
- Electricity produced on dissimilar materials through physical contact & separation
- Out going material negative, remaining material positive.
Spontaneous combustion:
The ignition of material brought about by a heat producing exothermic chemical actin within the material itself, without exposure to an external source of ignition. (Wet oily rags, wet saw dust)
Armature reaction.
– When a D.C generator or a motor is operating with load, sparking between the carbon brushes and the commutator results due to Armature Reaction. Armature reaction takes place when the armature current flows in the armature.
– When current flows in armature, the armature core is magnetising by this current. Magnetising effect of the armature current can be divided into two effects: –
- Cross magnetising or distorting effect.
- Demagnetising or weakening effect.
To compensate the Armature reaction, modern Electrical Machines are provided with
- Interpoles
- Carbon brush rocker.
- Neutralising Winding.
A.C motor starters:
A motor starter is an apparatus used for controlling the starting of an electric motor.
- Direct on line starter.(without current limiting element)
- Resistor or rheostatic starters.(with current limiting device)
- Star delta starter.
- Auto Transformer starter.(reduced voltage starting 55%, 60%, 70%, full voltage running
- Rotor resistance starter.(starting slip ring induction motor)
Dash pot
Mechanical device to produce a time delay action. Operation of switch gears, arc lamps, motor starters, Electro magnetic bake, etc. Time delay is adjusted by oil viscosity used.
Earth detecting lamps
- The earth fault detector consists of three incandescent lamps which are connected in star. These three lamps are supplied from the secondaries of three single phase step down transformers. The primaries of three transformers are connected in star. The star point of the primaries is connected the frame of the ship. The primaries of these transformers are fed from the red phase, yellow phase and blue phase of the ship supply.
- Giving visual signals and buzzer will sound when there is an Earth fault in the system on board.
- Three incandescent lamps which are connected in star. These three lamps are supplied from the secondaries of three single-phase step down transformers.
- The primaries of these three transformers are connected in star. The star point of the primaries is connected the Frame of the ship. The primaries of these transformers are fed from the Red phase, Yellow Phase and Blue Phase of the ship supply main.
- No Earth Fault in the system, Lamps will glow with equal brightness.
- When earth fault occurs one of the phases, the lamp on that phase will become dark and other two lamps will burn with extra brightness.
- Earth fault can be traced by switching off the branch circuit breaker one by one. When the branch circuit with the fault is switched off, the earth lamp will return to its normal glow.
Emergency power supply:
- Emergency lights.
- Navigation lights.
- International communication equipment.
- Day light signalling lamp.
- Ship’s whistle.
- Fire detecting and alarming installation.
- Manual fire alarm.
- Other internal emergency signal.
- Emergency fire pump.
- Steering gear.
- Navigation aid and other equipment.
Single phasing:
- Single phasing is the term used to denote the condition arising in a three-phase circuit when one phase becomes open circuited.
- The open circuit in a phase, often from a blown fuse, faulty contact or broken wire, will prevent a motor from starting but running motor may continue to operate with a fault.
- Excessive current in the remaining supply cable.
- Unequal distribution of current in motor winding.
- Can be detected by overload device in the supply line or through the overheating.
- Overheating in a stalled or running motor will cause burn out of the overloaded coil.
- In a lightly loaded motor to remain undetected by electromagnetic trips on the supply line which monitor only current. Improve protection is given by thermisters placed in the winding to measure thermal effects.
Insulated neutral system
Advantages
- This system avoids the risk of loss of essential services e.g. steering gear
- If the neutral was earthed and a short circuit on one phase causes the fuse in that phase to blow the system would now be singled phasing and may burn out motors
- In an insulated neutral, one earth fault does not interrupt the supply but an earth leakage detection system will give warning.
- Low earth fault currents in insulated systems gives a much less fire risk.
Disadvantages
- On the insulated system the voltage to earth is 1.73 Vph e.g. 440v vs 250v
- Tracing an earth fault is more difficult because although selective tripping may trace the earthed circuit, the actual position on the circuits may still be difficult to locate. Resonant or intermittent faults in say a contactor solenoid or a transformer with an insulated neutral can cause voltages to be magnified to say 4 times the normal voltage to earth (250v x 4 = 1000v)
Note: electrical shock is not reduced by using a non-earthed neutral as large voltages are involved. Both systems are equally dangerous
Earthed neutral system
When an earthed neutral system of generation is used earthing is to be through a resistor. The resistor is to be such that it limits the earth fault current to a value not greater than the full load current of the largest generator on the switchboard section and not less than three times the minimum current required to operate any device against
Back E.M.F
- When a current flows through the conductors of an armature of a motor, a force will be exerted on the conductors. This force produces a torque, which will cause the armature of the motor to rotate.
- When the armature conductors are moving across the magnetic field, these conductors will cut the magnetic lines of force and therefore generate an E.M.F. The direction of this generated E.M.F is opposite to the applied voltage of the motor. Since the generated E.M.F in the motor is opposite to the applied voltage to the motor, this E.M.F is called Back E.M.F.
Applied Voltage = Voltage drop to armature resistance + Back E.M.F
V = Ir + Eb
Automatic voltage regulator (AVR):
Sudden load current surges (sudden great increase) (e.g. due to motor starting) on a generator cause a corresponding change in its output voltage. This is due to an internal voltage drop in the generator ac windings and the effect is usually called ‘voltage dip’. Similarly, load shedding (to get rid of it) will produce an over voltage at the bus-bars. An unregulated or non-compounded generator excitation system would not be realistic on board ship due to the varying voltage caused by the fluctuating load demand. Automatic voltage regulation (AVR) equipment is necessary to rapidly correct such voltage change.
- Carbon pile regulator.
- Vibration contact regulator.
The alternator output is transformed, rectified and output effect through magnetic coil against spring which are voltage reference and apply to dc exciter shunt field and rotor of alternator.
- Static automatic voltage regulator.
The direct current derived from the alternator output through transformer & rectifier, is applied to a bridge which has fixed resistances on two arms and variable resistances (zener diode voltage references) on the other two. When change in applied voltage, by Whetstone bridge produce an error signal. The error signal can be amplified and used to control alternator excitation in different ways. (Thyristor, Transistors in series)
Diode
- An electronic device that allows electrons to flow in one direction but in highly resistant to current flow in the opposite direction. (Similarly check in the piping system.)
- The purpose of the diode is to function as a rectifier of higher frequency and low frequency oscillation. It is used as detector in a receiver circuit.
- Thermionic diode consists of a heater, a cathode and an anode, in an indirectly heated valve.
- Semi conductor diode is constructed with Mono crystalline germanium or silicon wafers with two layers differently doped; ‘pn’ junction acting as rectifier junction.
Transistor
- Three layer device, either NPN or PNP
- It has emitter, collector & base
- Used small signal power from a side circuit controlling the larger power in other circuit. (Power gain or amplification)
Thyristor
- Power control element. Multi -layer device of alternate P and N junction.
- E.g. Silicon controlled rectifiers (SCRs) ~ Four layer device.
Triacs ~ Greater number.
- Thyristors are solid state switches, which are turned on by application of a low-level signal voltage through a trigger connection known as a gate electrode
- No moving parts to wear, or contacts which can be damaged by arcing.
- Ideal for remote operation. Small size ~ convenient component of control circuit. Can control current greater than 1000 amps and voltage in excess of 1000 volts. Replace large conventional switches.
- Operate faster rate (25,000 times per second).
Exciter:
- It is a small D.C generator. It supplies the exciting current to the rotor of the A.C generator.
- Exciting current is current required to create any magnetic field.
Equaliser
An equaliser is a connection between the generators of different capacities running in parallel so that the running load is divided proportionately between the two.
D.C loads on A.C ship service system:
- General alarm system.
- Emergency lighting.
- Emergency radio power.
- Rectifying for battery charging.
Maintenance of motors:
- Keep air passage clean.
- Remove deposits of dust, oil and grease.
- Take insulation resistance reading.
- Prevent sparking at brushes and commutator.
- Mechanical check at bearings, holding bolts couplings.
- Regular check on motor starters and controllers, maintenance of contacts, resistance and connection.
Galvanometer:
It is an instrument for measuring the small electric current with its magnitude and direction.
Resistor:
It is a device, which conducts electricity but converts part of the electrical energy into heat.
Resistivity:
It is a resistance of a material and expressed in ohms/unit length.
Rheostat
It is a resistor, which is provided with means for readily adjusting its resistance.
Fire fighting at switchboard
- First of all the circuit breaker to be break out. Then extinguished with the fire with CO2 portable extinguisher.
- After fire is stop, the switch board is cool down
- All wire system must be traced and continuity test.
- After tracing and renewing all fittings, the switchboard can be put back into service.
Fire Prevention:
- Use correct fuse.
- All contacts of circuit breakers and switches are well contact.
- All wire connections are well lapped.
Causes of Fire:
- Loose contact.
- Incorrect fuse.
- Insulation break down
Residual magnetism:
When starting up a generator, the necessary magnetism is provided by the iron cores of the field poles. This magnetism is known as residual magnetism.
Battery installation and safety measures:
- Require good ventilation for H2 involving. Require suitable paint to outlet vent ducts. Ventilation inlet should be below battery level.
- Naked light and smoking are prohibited in battery room.
Lap wound. Multi parallel circuit in armature.
Wave wound Two parallel circuit in armature.
Failure to excite:
- Loss of residual magnetism.
- Too high resistance in the field circuit.
Universal motor:
- Series wound.
- Single phase.
- Either A.C or D.C can be used.
- Fractional(very small) power. (Less than 1 HP.)
Used on sewing machine, portable drill, etc.
(When the motor is attached to D.C line, the current is in the same direction all the time. In an A.C line the current is reversing itself every cycle.)
What are the likely consequences of attempting to close the incomer’s Air Circuit breaker (ACB) when the generators are not in synchronism?
At the instant of closing the breaker, the voltage phase difference causes a large circulating current between the machines which produces a large magnetic force to ‘pull’ the generators into synchronism. This means rapid acceleration of one rotor and deceleration of the other. The large forces may physically damage the generators and their prime movers and the large circulating current may trip each generator breaker. Result? Blackout, danger and embarrassment!
Synchronising:
- Synchroscope
- Synchronising lamp:
- ‘Dark’ lamp method. (2 lamps)
- ‘Bright’ lamp method. (2 lamps)
- ‘Sequence’ method.(3 lamps)
How could you monitor the correct instant for synchronising without the aid of a Synchroscope or synchronising lamps?
Connect pair of 500 V voltmeter probes across one phase of the incoming machine circuit breaker. Adjust the generator speed until the voltmeter slowly fluctuates from zero to maximum. Close the breaker when the voltmeter passes through zero.